Digital Subtraction
Subtraction is a technique used to obtain an image in which only the difference of the two original images remains visible. This technique is mainly used in angiography.
Digital subtraction?
Digital subtraction, is subtraction made by processing digital images. Usually the computer connected to the device used to do angiography does this automatically. However, it is possible to change some parameters in the process, such as the choice of reference image. This is to avoid as much motion artifacts as possible.
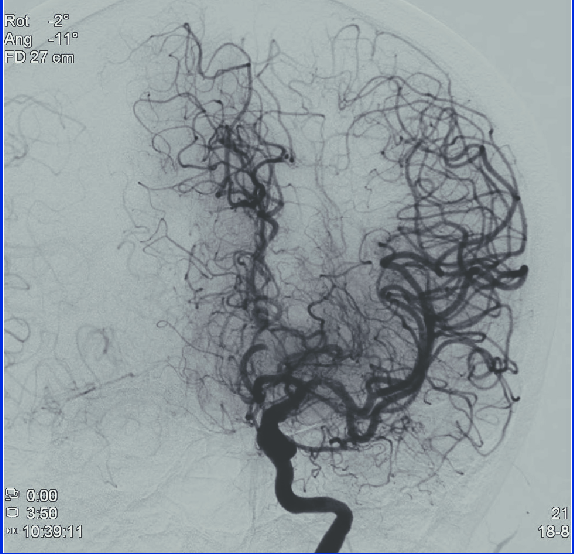
How does subtraction work?
When recording for angiography, a reference image is started before any contrast agent has been administered to the patient. This image is preserved. Now when we administer a contrast injection and re-expose images, we start to see not only the reference image but also the elements that are passed through by the contrast substance. We will then subtract, or subtract, the reference image from the obtained image with contrast filling. We then retain an image in which blood vessels can be clearly seen, while bones, etc. appear to have been swept away. However, this system is also sensitive to patient movement.
Example:
The following example shows a schematic representation of what subtraction is and how it works. The first image represents a reference image, that is, an image taken before contrast administration. The second frame is that same image, but where the + image represents the contrast fill. The third image then again is what is obtained when subtraction is applied. The first image is subtracted, as it were, from the second, thereby leaving only the difference between the two images.
 |  |  |
| Reference photo, without contrast | same image as reference photo but now with contrast | Difference between the two pictures = just the contrast |